There are numerous standards defined over the past several decades to govern data wiping and other data destruction techniques for safe and compliant media sanitization practices. For data erasure, these standards determine the overwriting patterns and passes set by government agencies and private institutions across the world.
The DoD 5220.22-M wiping standard was published by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) in the National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual (also known as NISPOM or Department of Defense document #5220.22-M). The DoD standard was developed in 1995 for high-security institutions like the Pentagon, etc. At the time of its launch, the standard had set a benchmark for data wiping and hardware disposal with its DoD Information Assurance Certification and Accreditation Process (DIACAP).
This article provides insight into the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) 5220.22-M standard for drive erasure. It also deep dives into the steps involved in the US DoD data wipe standard for sanitizing media, memory, and drives in equipment. Further, it provides guidance regarding sanitization (data destruction) and disposition of the most common media used (e.g., hard drives) and equipment used for classified processing. The Clearing and sanitization matrix is explained as per the NISPOM manual.
What is the DoD 5220.22-M Standard?
DoD 5220.22-M Standard is a widely recognized method for data sanitization used by organizations, including government agencies worldwide, for performing drive erasure. In the media sanitization circles, it is known as the US DoD data wipe standard. The standard involves overwriting the previously stored information on a hard drive with specific binary patterns repeatedly (3 times or 7 times) depending upon the number of passes defined in the organization’s policy.
The DoD method is based on overwriting the addressable memory locations in hard disk drives with 'zeroes' and 'ones' as binary patterns. The standard defines the implementation of three secure overwriting passes with verification at the end of the final pass.
The following passes constitute the US DoD data wipe standard:
Pass 1: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary zeroes
Pass 2: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary ones
Pass 3: All addressable locations are overwritten with a random bit pattern
The final overwrite pass is then verified.
In 2001, DoD published the DoD 5220.22-M ECE method, a 7-pass version of the original standard. It runs DoD 5220.22-M twice and an extra pass (DoD 5220.22-M (C) Standard) in between.
Pass 1: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary zeroes
Pass 2: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary ones (the compliment of the above)
Pass 3: All addressable locations are overwritten with a random bit pattern
Pass 4: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary zeroes
Pass 5: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary zeroes
Pass 6: All addressable locations are overwritten with binary ones (the compliment of the above)
Pass 7: All addressable locations are overwritten with a random bit pattern
Verify the final overwrite pass.
Despite the upgrades, the three-pass method is still the standard implementation for DoD-level data wiping. However, the NISPOM official manual, ‘Page 122,’ requires organizations to follow NIST SP 800-88 Rev 1 Guidelines for Media Sanitization when making practical sanitization decisions based on the level of confidentiality of information (especially for SSDs, hybrid drives, etc.).
Why Use the DoD 5220.22-M Wiping Standard?
The DoD 5220.22-M data wipe algorithm is widely recognized as a leading method for data destruction, maintaining its status as an industry standard for hard drive erasure in the U.S. The DoD 5220.22-M data wipe standard performs verification at the end of each pass. This ensures that the data is duly overwritten. In addition to zeroes and ones, DoD 5220.22-M uses random characters to overwrite the storage locations on a hard drive. The inclusion of random characters reduces the probability of data recovery. However, for high-capacity hard drives or large inventories of storage drives, this method is more time-consuming than NIST Clear or NIST Purge methods. Additionally, a 3-pass wipe using the DoD standard can shorten the lifespan of SSDs compared to the one-pass wipe prescribed by NIST Clear.
According to the Defense Security Service (DSS) Assessment and Authorization Process Manual (DAAPM) Version 1.3, released on June 4, 2018, the Media Sanitization Matrix below outlines appropriate methods to be used for Destroying Media as per the media type. The table below shows the approved method for sanitizing different media types.
Further, the NISPOM Operating Manual (Incorporating Change 2, May 18, 2016) specifies in Section 3, Security Controls, 8-302(g(3)) Media Protection: “Sanitize or destroy ISs media before disposal or release for reuse in accordance with procedures established by the CSA.”
Clearing and Sanitization Matrix
|
Media
|
Clear
|
Sanitize
|
Order
|
|
Magnetic Tape
|
|
Type I
|
Degauss
|
Degauss
|
-
|
|
Type II
|
Degauss
|
Degauss
|
-
|
|
Type III
|
Degauss
|
Degauss
|
-
|
|
Magnetic Disk
|
|
Bernoulli
|
Degauss or Overwrite
|
Degauss
|
-
|
|
Floppy
|
Degauss or Overwrite
|
Degauss
|
-
|
|
Non-Removable Rigid Disk
|
Overwrite or Degauss
|
Pattern Overwrite
|
-
|
|
Removable Rigid Disk
|
Degauss or Overwrite
|
Pattern Overwrite
|
-
|
|
Optical Disk
|
|
Read Many, Write Many
|
Pattern Overwrite
|
-
|
-
|
|
Read Only
|
-
|
Destroy if classified information is present
|
-
|
|
Write Once, Read Many (WORM)
|
-
|
Destroy if classified information is present
|
-
|
|
Memory
|
|
DRAM
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
-
|
|
EAPROM
|
Chip Erase
|
Chip Overwrite
|
-
|
|
EEAPROM
|
Chip Erase
|
Random Overwrite
|
-
|
|
EPROM
|
UV Erase
|
Triple UV Erase and Overwrite
|
Triple UV Erase followed by Overwrite
|
|
FEPROM
|
Chip Erase
|
Chip Erase and Overwrite
|
Chip Erase followed by Overwrite
|
|
PROM
|
Overwrite
|
-
|
-
|
|
Magnetic Bubble Memory
|
Overwrite or Degauss
|
Overwrite
|
-
|
|
Magnetic Core Memory
|
Overwrite or Degauss
|
Pattern Overwrite
|
-
|
|
Magnetic Plated Wire
|
Overwrite
|
Overwrite and Long Overwrite
|
Overwrite and Long Overwrite
|
|
Magnetic Resistive Memory
|
Overwrite
|
-
|
-
|
|
NOVRAM
|
Overwrite
|
Overwrite
|
-
|
|
ROM
|
-
|
Destroy
|
-
|
|
SDRAM
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
-
|
|
SRAM
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
Overwrite or Remove Power
|
-
|
|
Other Media
|
|
Video Tape
|
-
|
Destroy
|
-
|
|
Film
|
-
|
Destroy
|
-
|
|
Equipment
|
|
Monitor
|
Remove Power
|
Screen Destroy
|
-
|
|
Impact Printer
|
Remove Power
|
Destroy Ribbons
|
Destroy Ribbons then Remove Power
|
|
Laser Printer
|
Remove Power
|
Run Page
|
Run Page then Remove Power
|
Destruction of the media is an approved Sanitize method for all media types mentioned below, except for Equipment (Monitor, Impact Printer & Laser Printer). Destruction is only mentioned specifically where it is the sole method of 'Sanitize'. The Order column is only applicable when a combination of two procedures is required to sanitize the media.
Note: We have abbreviated the sanitization methods for your easy understanding. Their actual meaning is given below per DAAPM Version 1.3.
- Degauss: Degauss media using a Type I, II, or III degausser.
- Overwrite: Overwrite each addressable location with a single character using an approved overwrite utility.
- Pattern Overwrite: It is for spills only, first overwrite with a pattern, followed by its complement, and then with another unclassified pattern. However, sanitization is considered to be complete only when three cycles are done. Verification of the sample is necessary. If during verification any part of the disk is found to be un-writable or inaccessible, then destroy or degauss the disk.
- Remove Power: Remove the power source, including any connected batteries.
- Chip Erase: Perform a full chip erase as per the manufacturer's instructions.
- UV Erase: Perform an ultraviolet erase as per the manufacturer's recommendation.
- Chip Overwrite: Perform Chip Erase, then perform Overwrite a total of three times.
- Random Overwrite: Overwrite all locations first with a random pattern, followed by binary zeros, and then with binary ones using an approved overwrite utility.
- Triple UV Erase: Perform an ultraviolet erase as per the manufacturer's recommendation, increasing time by a factor of three.
- Long Overwrite: Each overwrite must reside in memory longer than the time classified data resided in it.
- Destroy Ribbons: Ribbons have to be destroyed, and Platens have to be cleaned.
- Screen Destroy: Inspect and test the screen surface for evidence of burn-in information. If the information is present, then the screen must be destroyed.
- Run Page: Run 1 page (font test acceptable) when the print cycle is not completed (e.g., paper jam or power failure). Dispose of output as unclassified if visual examination does not reveal any classified information.
To Wrap Up
DoD 5220.22 data wipe standard still carries a lot of credibility and is held in high esteem as it provides a robust 3-pass erasure that is detailed and efficient. This standard is meaningful for wiping PC, laptop, HDD, SSD, etc. NIST 800-88 is recommended by DoD for wiping classified, confidential information from newer media like NVMe drives, hybrid drives, etc. Many government institutions follow both DoD and NIST standards as components of their drive erasure and data disposition policy to reuse, recycle, and reallocate media and achieve an organization’s sustainability goals.
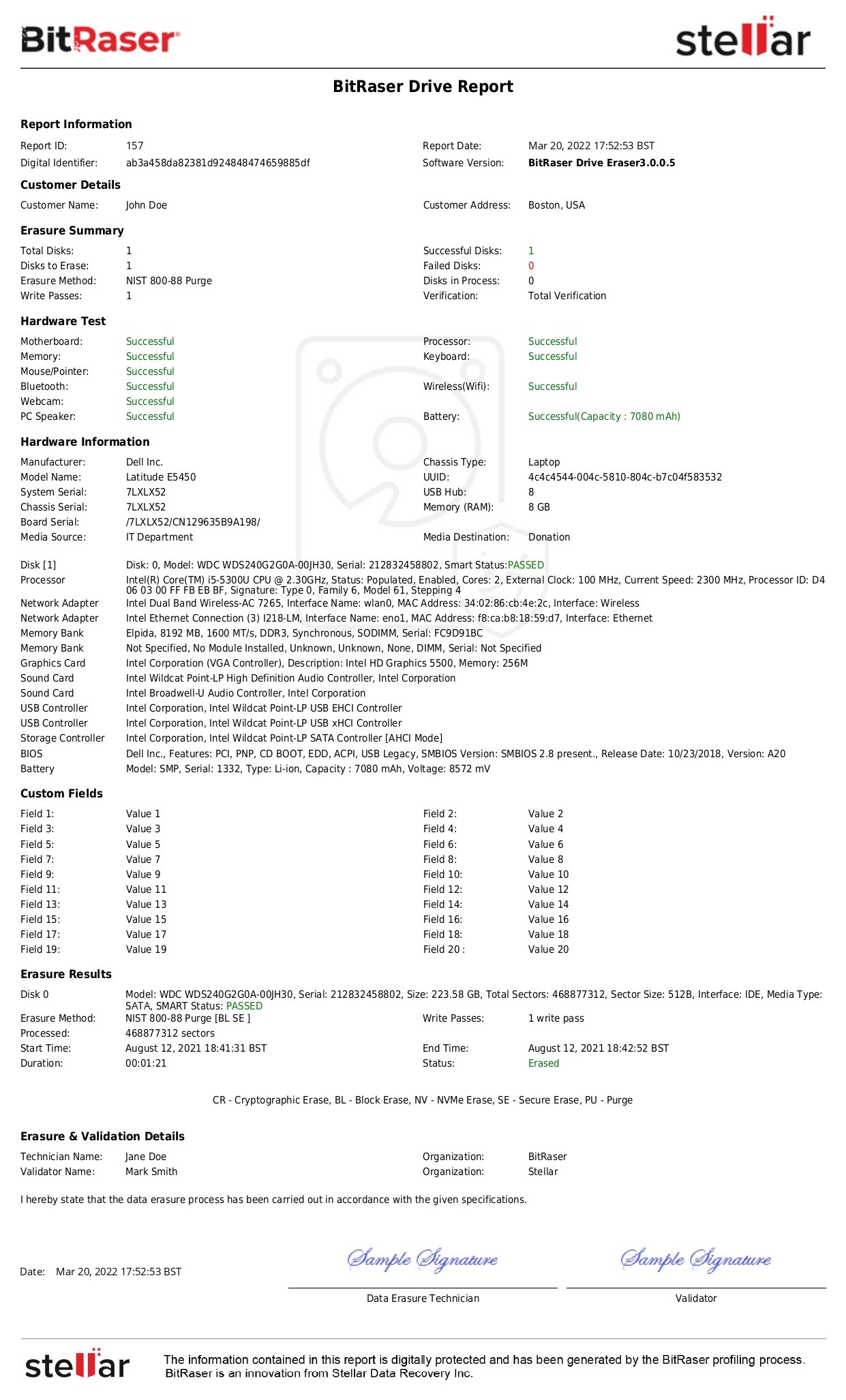
DoD compliant data wipe software tools such as BitRaser Drive Eraser help erase the hard drives, SSDs, PCs, laptops, and Macs as per the DoD and NIST standards. This software generates tamper-proof certificates and reports for audit trails and helps attain regulatory compliance with data privacy laws and regulations like CCPA, SOX, GLBA, FACTA, PCI-DSS, EU-GDPR, etc.