Summary: Data wiping is the process of erasing the data from a storage device beyond recovery. The process involves overwriting the storage device – laptop, desktop, servers, loose drives, SSDs, bulk drives, or mobile devices in an illegible way. The procedure makes it impossible to recover data, even after using reliable data recovery software or in-laboratory services. So, if you are planning to sell or donate your storage device, wipe the device using secure data sanitization software to avert data breaches.

Data wiping is not as easy as deleting or formatting a storage device (be it hard drives, SSDs, bulk drives, or mobile devices). Data deletion or drive formatting does create free space in your device, but that does not ensure the destruction of the data. It simply hides the data files to give you free space for further storage. A freely available DIY data recovery software can get the data back after an episode of quick formatting or deletion.
Let’s understand the different types of data-wiping methods.
Types of Data Wiping
The data wiping process involves overwriting the device with a stream of unintelligible characters, like 0s and 1s, at all user-addressable locations leading to permanent sanitization of the device beyond recovery. The technique is backed by global data overwriting algorithms. The most prevalent types of data wiping as defined by various International bodies, like NIST, and DoD, include:
- 1 Pass Data Wiping
Single-pass data wiping overwrites all addressable memory locations with binary 0s. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-88 Clear standard, it is sufficient to erase data from devices beyond recovery.
- 2 Passes Data Wiping
The dual passes permit erasing of the data on addressable memory locations with binary 1s.
- 3 Passes Data Wiping
This multiple pass data wiping enables overwriting with a random bit pattern, with a verified final overwrite pass.
- 4 Passes Data Wiping
The Canadian RCMP TSSIT OPS-II sanitization method was published in 1997. It involves 4 passes of overwriting - the first three passes include a cycle of alternate 1s and 0s and the fourth pass comprises random characters.
- 33 Passes Data Wiping
As per the Pfitzner method, 20 passes of overwriting leave the possibility of data recovery. However, using a complex algorithm of 33 passes with a combination of random characters for each pass, successful data wiping is possible. - 35 Passes Data Wiping
Another algorithm developed by Peter Gutmann, in 1996, works by overwriting some random values with 35 passes. In this kind of data wiping, pseudo values are used for the first and last 4 passes followed by a complex pattern in each pass that lies between the range of 5 to 31.
To acquire an in-depth knowledge of Standards and Methods of Data Wiping, refer to our article that elaborates on the international standards for data erasure. You may also like to refer to our article on choosing the right erasure standard to strategize your data destruction plan.
Key Benefits of Data Wiping
Besides protecting confidential business data and preventing data leakage, data wiping through overwriting techniques enable the users to resale and recycle the storage device. There are numerous benefits of secure data erasure. Let’s take a gander at the most significant ones:
- Helps Reduce E-Waste
Enterprises and Service Providers have an obligation by law to advocate environment-friendly solutions to minimize e-waste. Data wiping through software is an eco-friendly solution that plays a major role in the end-of-lifecycle of IT assets. Secure data destruction is the primary step to mitigate the risks of data breaches.
- Gives Peace of Mind
Perhaps one of the most prominent reasons to invest in a certified data-wiping tool or service is the guaranteed destruction of data beyond retrieval. A tamper-proof audit trail is a license for zero data leakage by the end of the IT assets lifecycle. Once invested in a reliable solution, enterprises and government bodies can take gasp signs of relief without losing minds over possible future data breaches.
- Promotes Reuse, Resale, and Refurbish
By sanitizing the storage device, the device becomes reusable and available for resale in the refurbished market. IT asset managers can resell the old device without having the fear of a data breach once the device is sanitized using secure data-wiping software, like BitRaser. Likewise, they can avail the services of an IT Asset disposition company that helps in sanitizing the media and provide audit trails.
- Attain Regulatory Compliance
Another vital reason for data wiping is the need to adhere to data destruction policies and meet regulatory compliance. Professional service providers give a certificate and audit trail that guarantees permanent data erasure.
In a nutshell, there are many benefits of capitalizing a reliable data erasure software. However, often users get distracted by the lucrative free or unreliable options available in the market. Despite self-proclaimed statements on using certified data erasure techniques, they leave a major gap in the probability of delivering failsafe certificates for data erasure and meeting compliance.
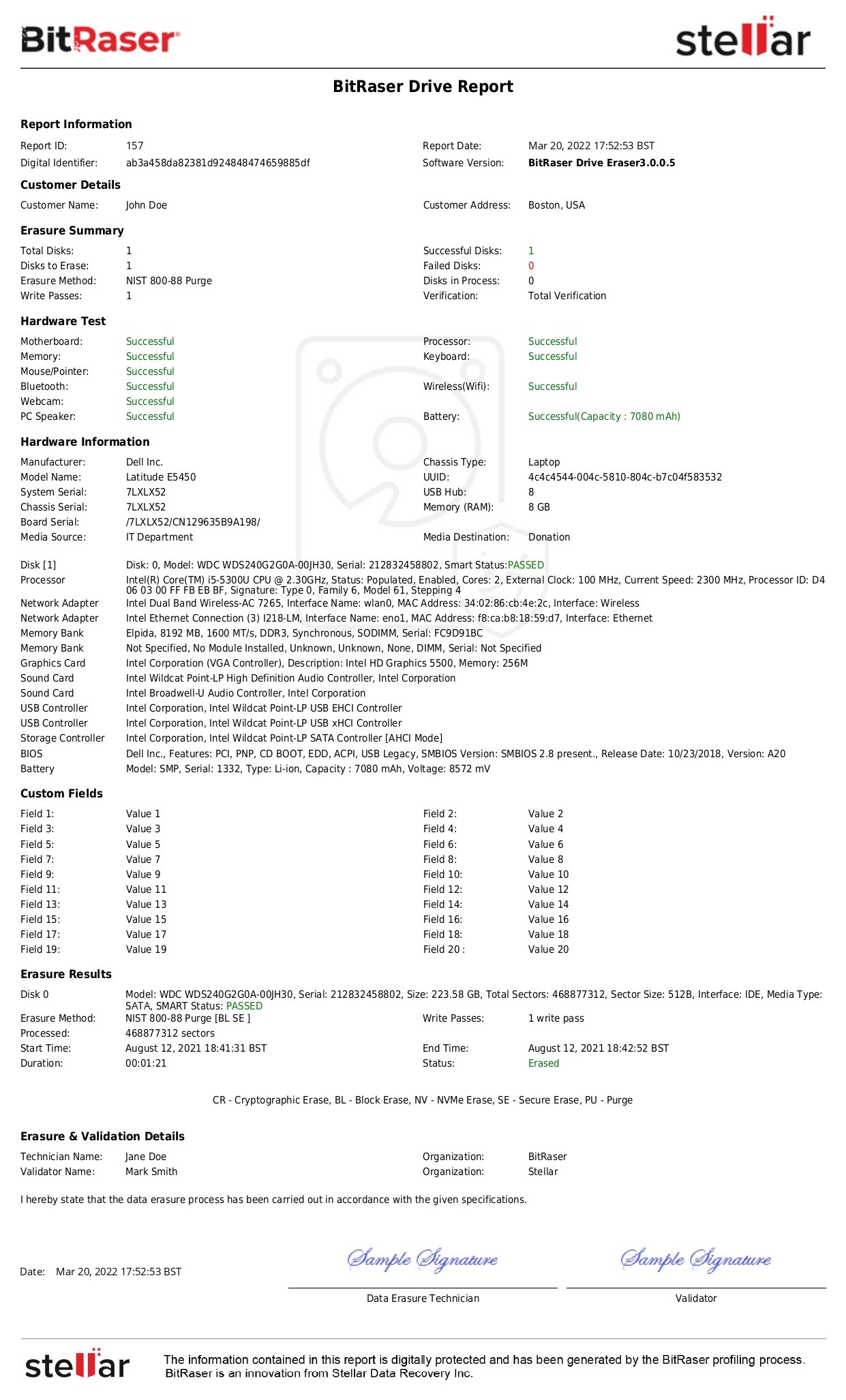
So, look for a steadfast, specialized forensic test, designed exclusively by a standardized lab. The NIST-led computer forensic tool testing of BitRaser Drive Eraser demonstrates and reaffirms the advantages of a reliable data erasure tool. It can wipe the hard drive or SSD as per NIST SP 800-88 standard.
In the present scenario of remote handling of IT assets post-pandemic (Covid-19), an exponential surge of unmanageable data is observed. Secure data wiping is a vital necessity for businesses to prevent data leakage and other possibilities like data fraud, identity theft, brand damage, and litigation.
As explained in this article, all storage devices transition through a discrete lifecycle before leaving their possession. So, it is the duty of data collectors and users to avert evident risks of leakage at all stages of IT assets management to lead the way for secure data usage.
Why Data Wiping is a Necessity?
Data wiping is a necessity for ITADs and refurbishing companies that deal with the bulk erasure of storage devices. They need a scalable and automated data erasure solution like BitRaser to meet their end customer data sanitization needs, following global laws and regulations like SOX, GLBA, GDPR, and HIPAA.
Likewise, large enterprises, government bodies, or small businesses need a robust data erasure solution to protect their customers’ data privacy when putting the IT device to rest. Data wiping needs are prevalent across industries, be it banking, automobile, healthcare, manufacturing, insurance, etc. The enterprises in these industries accumulate a great volume of customer data over the years. So, they need a tailored solution to safely destruct the data stored in old devices.
Furthermore, independent smartphone and laptop users are keeping highly sensitive banking details saved online. It poses a significant threat to their privacy that may eventually cause unbearable financial losses. To prevent such probable complications, a secure data-wiping solution is the need of the hour.