The National Health Service (NHS) is the UK’s healthcare system that provides healthcare services regardless of the legal resident’s ability to pay. It manages massive data volumes comprising personal health data, including name, address, email ID, date of birth, NHS Number, National Insurance Number, etc. Given the volume of sensitive data handled by the NHS, it’s essential to have secure policies that provides guidance on personal data handling.
NHS England and NHS Improvement established a joint enterprise that enforces the NHS Data Protection Policy (Version 5.1, 2019). This policy adheres to both the UK GDPR and the Data Protection Act 2018, and aims to ensure lawful and proper treatment of personal data.
Scope of NHS Data Protection Policy
The policy is applicable to the staff of the NHS and the employees of their partner agencies, vendors, or contractors who have access to confidential patient information.
To follow data protection laws properly, the official NHS organisations (NHS England and NHS Improvement) entered into a contract called the Joint Controller and Information Sharing Framework Agreement. This explains how the NHS shares responsibilities for protecting data and the steps taken to make sure the rules are followed, including:
- Appointments of a joint Data Protection Officer (DPO) & a joint Senior Information Risk Owner (SIRO).
- Collaboration for conducting data protection impact assessments.
- Sharing an information asset register.
- Work together to give clear privacy information to data subjects.
Data Protection Principles
NHS Data Protection Policy is guided by the six core principles, as mentioned in Section 1.3. These principles guide how personal data should be processed. It states that data should be:
- Processed lawfully, fairly, and transparently
- Collected for clear and legal purposes
- Limited to what is necessary for the purpose (Rule of Data Minimisation)
- Accurate and kept up to date
- Kept only for as long as needed for the purpose of its collection
- Kept secure through appropriate technical & organizational safeguards
The data protection principles apply to both hard copies and digitally stored information. In terms of data security, the sixth principle becomes particularly important when sensitive data-bearing devices leave organisation's premises or control. For instance, when laptops are discarded, it’s essential to securely erase all data from the drives as per Sec 3.3 of Employee Responsibilities.
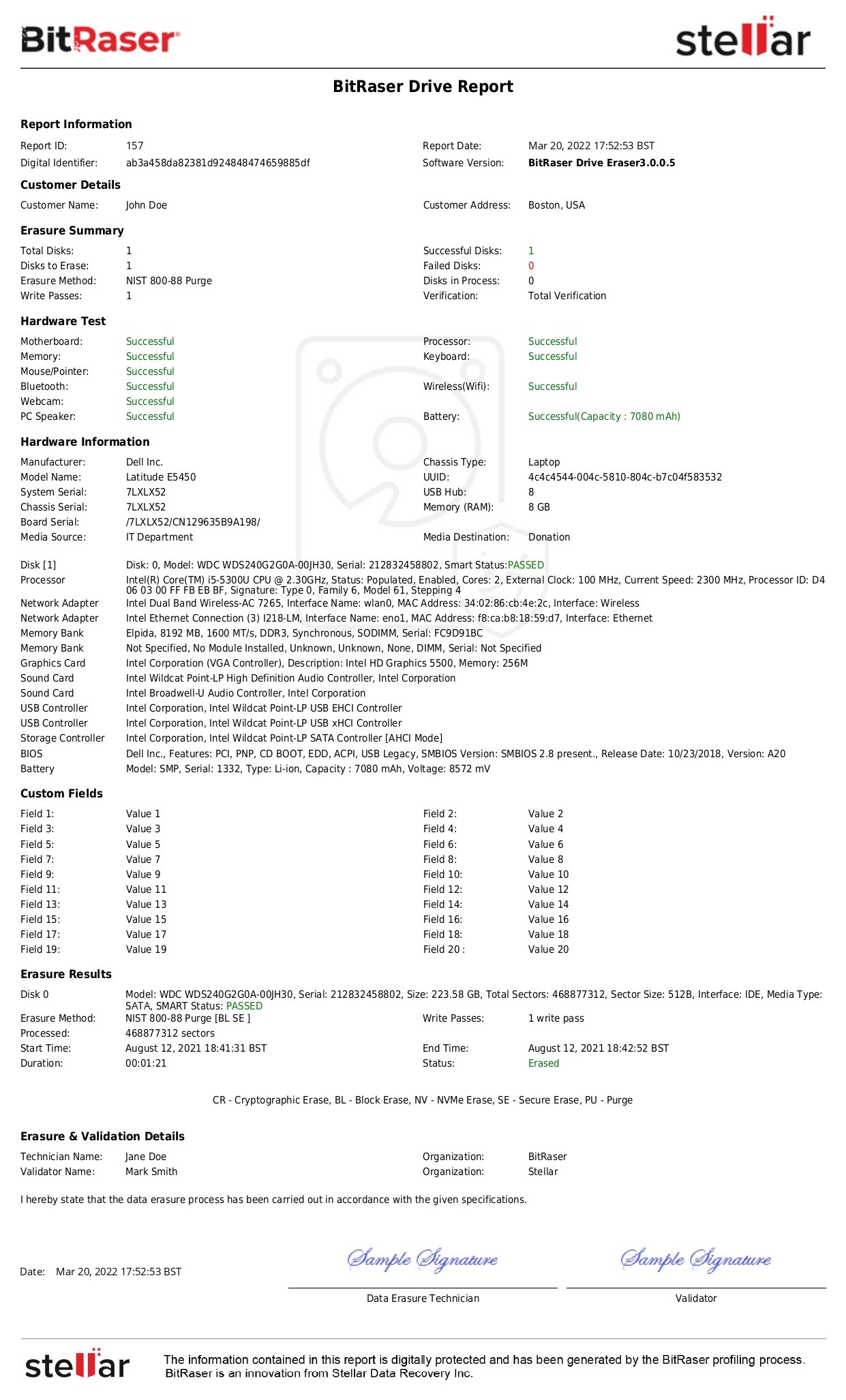
The NHS refers to the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) for guidance on the disposal of personal or sensitive data-bearing media devices. The NCSC recommends methods like overwriting all memory locations with non-sensitive patterns to ensure data is irretrievable. Overwriting can be done using software tools like BitRaser. The purpose of sanitisation, according to the NCSC, is to render data irretrievable. It further requires that any devices leaving the organisation’s control must be sanitised before they do so.
Information Covered Under NHS Data Protection Policy
NHS Section 1.4 covers any data that can identify a living individual as per the definition of ‘personal data’ under GDPR, including pseudonymized data that includes name, address, phone number, Email address, NHS number, NI number, etc. It also covers special data pointers such as:
- Ethnic or racial data
- Political opinions
- Philosophical or religious beliefs
- Union membership
- Genetic, biometric, and health data
- Sexual history/orientation
- Criminal data
Roles and Responsibilities Under the NHS Data Protection Policy
The document further outlines the roles and responsibilities of NHS England and NHS Improvement through Section 3.1. These include the following:
- Enforcing the Joint Controller and Information Sharing Agreement.
- Supporting oversight roles like the SIRO and Caldicott Guardians.
[A Caldicott guardian is a senior person responsible for protecting the confidentiality of people’s health information and making sure it is used properly.]
- Providing training, guidance, and support to staff who handle personal information.
- Keeping records of processing activities for meeting compliance.
- Develop and maintain procedures to maintain compliance. These may include data protection impact assessment, managing responses to data subjects' rights requests, managing personal data breaches, etc.
Section 3.2 explains that the DPO is a mandatory requirement under UK GDPR. Data Protection Officer advises on compliance requirements, monitors policy effectiveness, acts as the point of contact for data protection matters, and reports to the SIRO and the board on matters related to data protection.
Further, as stated in Section 3.3, every NHS employee must:
- Follow all official policies and procedures.
- Understand the purpose for which the NHS uses the information.
- Respond appropriately to requests from data subjects.
- Avoid unauthorized disclosure or data export outside the United Kingdom.
- Ensure that data is securely destroyed when no longer required.
The policy states that non-compliance may lead to disciplinary action. It references Section 170 of the Data Protection Act 2018, which defines unlawful access or use of personal data as a criminal offence.
Distribution, Training, and Monitoring
As outlined in Section 4.1, the policy will be made accessible to all staff through the organisation’s intranet, with a notice issued via the staff bulletin. In Section 4.2, the focus is on training, where the Corporate Information Governance team, together with the DPO, will assess who needs training and provide the necessary support accordingly. Guidance will also be available on the intranet to help staff stay aligned.
Section 5 talks about how compliance will be monitored. Here, the Data Protection Officer and the Governance team will lead the process, supported by internal audit checks. The document review and updates will be handled by the Head of Corporate Information Governance every three years or earlier, if needed. Finally, Section 6 highlights the Equality Impact Assessment. The idea is to make sure the policy reflects NHS England’s ongoing commitment to fairness and inclusion.
This is a summarized version of the NHS Data Protection Policy. The full version is available on the NHS website.
Final Thoughts
The NHS Data Protection Policy helps ensure that sensitive information is handled securely with care and diligence. It provides a practical roadmap for lawful data handling, promotes accountability, and protects patient trust. UK Healthcare organisations, IT asset managers, and service providers can learn a lot from these NHS practices, particularly in areas like secure data destruction and compliance monitoring. Using tools that align with NCSC guidance ensures that no traces of personal data remain on old systems.
BitRaser is a certified data wiping software that permanently erases data from drives and devices, ensuring compliance with EU GDPR, UK GDPR, and other global data protection regulations.