Organizations take all possible steps to keep sensitive and confidential data safe. But security solutions and data privacy policies don’t always suffice. When devices change hands and move from higher security to lower security categories, it leads to the risk of data leakage. The device may now be used to store less or non-sensitive data, but the sensitive data stored in it earlier can leak from that device. The delete option in the devices makes data invisible to the naked eye. But it doesn’t remove it from the device. Freely available open-source DIY data recovery software can help people with malicious intent retrieve that data in no time.
Media sanitization is the only way to avoid data leakage from previously used media devices. Media sanitization can prevent organizations from adverse repercussions of data breaches and facing legal, social, and monetary consequences of such data breaches. The National Institute of Standards and Technology is a non-regulatory agency in the United States of America that issues guidelines and standards to help organizations avoid the repercussions of data leakage and breaches. NIST 800-88 Guidelines for Media Sanitization is a document formulated for this purpose that outlines the methods to be used for erasing data from media devices.
With the NIST SP 800-88 compliant media sanitization process, organizations and individuals can protect data privacy. The guidelines issued by NIST include information on the what, why, and how of media sanitization. There are three categories of media sanitization that can be used depending on the type of data and the device in question, namely NIST Clear, Purge, and Destroy. The guidelines help decision-makers in selecting a suitable category of sanitization. In order to know more about media sanitization techniques, you may refer to our article here.
In this article, we will discuss Clear techniques of media sanitization as outlined in the NIST 800-88 guidelines.
NIST 800-88 Clear Standard: An Insight
NIST 800-88 guidelines for media sanitization define the NIST Clear method as an approach to:
“Clear applies logical techniques to sanitize data in all user-addressable storage locations for protection against simple non-invasive data recovery techniques; typically applied through the standard Read and Write commands to the storage device, such as by rewriting with a new value or using a menu option to reset the device to the factory state (where rewriting is not supported).”
The Clear category for media sanitization thus applies logical techniques for data sanitization. It is suitable for all user-addressable storage locations. Simply stated, it replaces data with non-sensitive data in the media. It offers effective protection against simple and non-abrasive techniques of data recovery. Usually, the Clear techniques employ standard Read and Write commands. This includes rewriting new values to make the old values inaccessible. For example, if the original device contains information stored as a set of 0s and 1s, a new logic is applied which covers all the bits of information with 0. It is very similar to writing something on a piece of paper and then writing something over it to make the original text incomprehensible or non-restorable.
Another point to note is that overwriting isn’t applicable for damaged devices or devices that do not support rewriting. If a device is damaged, all storage locations on it may not be overwritten. This leaves gaping holes in the media sanitization process. In the case of devices that don’t support overwriting, the factory reset option available on the device may be used (as in the case of mobile devices). Factory resets are also a NIST-compliant Clear category technique if the device interface doesn’t have an option for data retrieval.
A majority of devices have Clear mechanisms in place for data sanitization, while the Purge mechanism is not as widely available in media storage devices.
Limitations of NIST 800-88 Clear Standard
The Clear technique should be used only when the device needs to be reused but won’t be leaving the organization. Also, NIST guidelines mention that media owners can choose the Clear techniques and accept its associated risks in case of moderate confidentiality data. However, in doing that, media owners must also acknowledge the risk that some data that has been sanitized using the Clear technique may be retrieved by someone who has the time, skills, and knowledge to retrieve it as sanitization with the NIST Clear technique does not address hidden or unaddressable areas.
Application of Clear Techniques on Different Storage Devices: NIST 800-88 Guidelines
Different types of devices need to be sanitized with different Clear category techniques. Popularly used device types and Clear techniques for them are discussed as below:
Hard Drives
The device should be overwritten using organizationally approved and validated methodologies, techniques, or tools. At least a single write pass is required for this method. For example, using all zeros. However, in some cases, multiple write passes or complex values may be used. After carrying out the Clear sanitization process, verification should be conducted.
SSDs
Clear sanitizing techniques for SSD drives require at least one write pass of writes with a fixed data value, such as all zeros. Overwriting on flash-based media (SSD) reduces its lifetime. If NIST Clear is used to erase data on a SSD then it may not sanitize data completely in unmapped physical media. This means some old data might still remain after the sanitization process is performed using the Clear technique. NIST Purge is the most recommended standard as per NIST 800-88 guidelines for erasing SSD.
Android Devices
For mobile devices, removable storage devices (like external SD cards) should be first unencrypted. They should then be removed before sanitization. Android OS devices should be plugged into a power source before starting encryption. (This is the first step of the Clear technique). The next step is performing a factory reset. The factory reset option is available in the Settings menu of the device. Refer to the user manual to find instructions for performing a factory reset on your device. Remote Wipe is another type of Clear sanitization technique. But it is impossible to verify the results of such a technique.
iPhones
For iPhones and iPads the Clear technique includes performing full sanitization. It stands true for both current and future-generation devices.
- Go to the Settings menu.
- Select the General option and click on Reset.
- Then select Erase All Content and Settings option.
Cryptographic Erase is supported on iOS devices. And encryption is on by default. Thus, the sanitization process takes just a couple of minutes. After sanitizing mobile devices, navigate to the different settings on the device for verification. Go to different menus in the device to check if you are still logged in to some of your accounts or if some specific settings that you made are still intact. This would mean the process didn't complete as intended and doesn't meet the NIST Clear standard.
With that, you know how Clear media sanitization works on different storage devices.
The Next Step: Verification of the Sanitization Process
As per NIST 800-88 guidelines, to maintain confidentiality, it is also important to verify that the information sanitization process has been performed correctly.
This verification can be done in two ways: The first type of verification is done when it is applied after every sanitization process, wherever applicable, as this type of verification is not practically feasible for most destroy techniques. The second type of verification is referred to as representative sampling, where verification is applied to a particular subset of media. Preferably the verification process should be done by individuals not involved in the original sanitization process.
NIST guidelines mention the following types of verifications that should be done:
- Equipment Verification: Involves scheduled maintenance and calibration of any equipment used in the sanitization process. It also includes workplace inspection.
- Personnel Verification: The individuals involved in the media sanitization process should be trained and experienced in the process. It should also be verified that they are well-qualified to use the required equipment for sanitization.
- Sanitization Result Verification: The most important aspect of verification involves ensuring that the data is effectively sanitized. Usually, verification involves checking all accessible areas for the expected sanitized value. Full verification is recommended if time and external factors permit. Otherwise, verification using sampling techniques can also be performed.
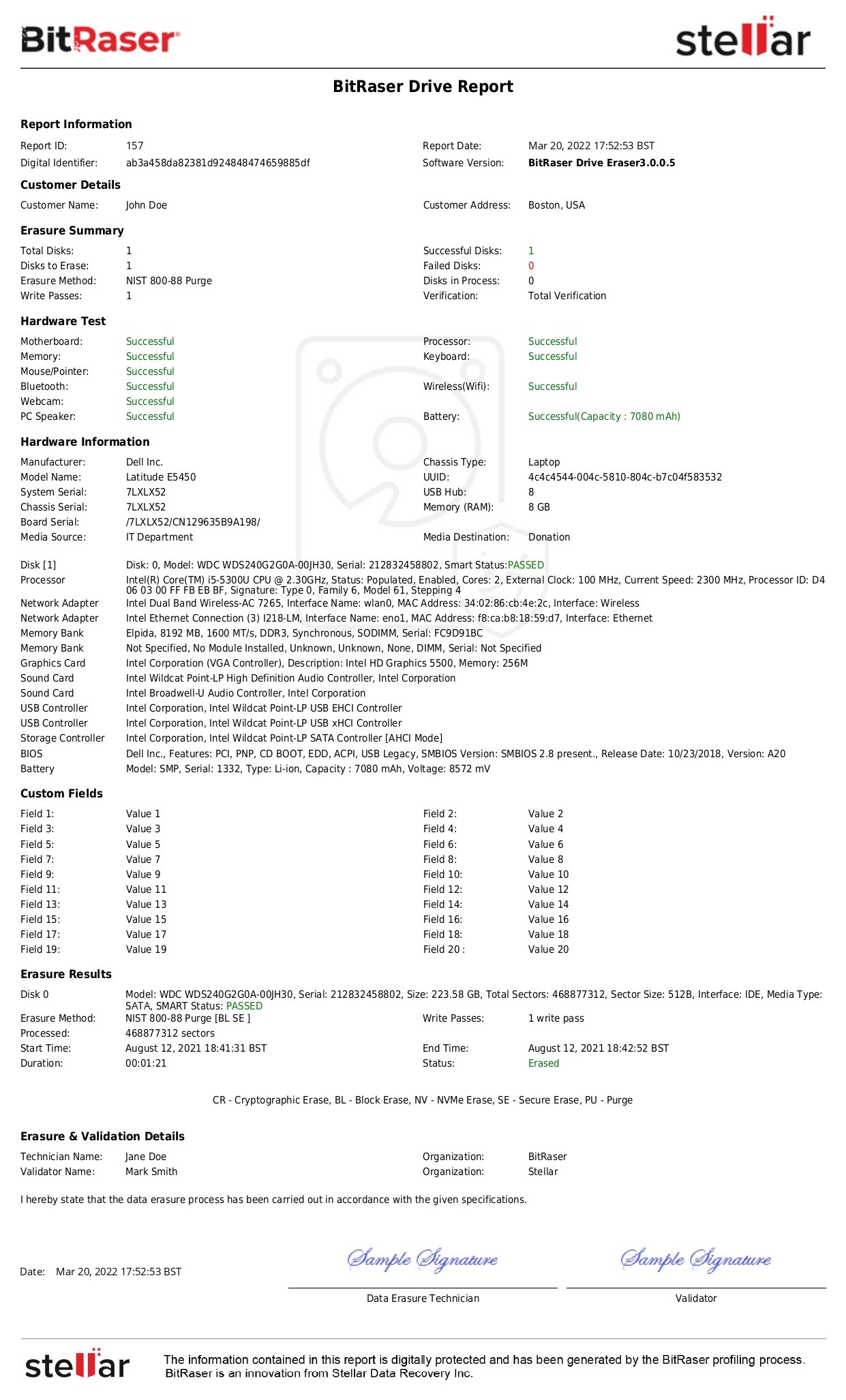
BitRaser Erases Devices Using NIST 800-88 Clear Standards; Ensuring Compliance with Global Laws
Now that the importance of NIST 800-88 compliance is established and the Clear technique has been discussed, the next step for you as an organization or an individual is to look for specialized solutions for media sanitization. While it is possible to carry out Clear media sanitization using a freely available tool, it isn’t in the best interest of the organization or individual as it does not guarantee media wiping efficacy and neither does it provide a certificate of erasure that is crucial for meeting compliance.
Professional software tools like Bitraser Drive Eraser help ensure regulatory compliance. With professional solutions, certificates of proper media sanitization and verification are guaranteed. In case of improper data disposal & handling accusations, lawsuits, and audits, such certifications act as proof of erasure. Specialized tools also limit human intervention due to increased automation. This further reduces the risk of breaches and data leakage. Another plus point of opting for commercial solutions is that they help comply with several other international data security and privacy regulations along with NIST 800-88.
BitRaser Data Eraser is a bespoke media sanitization solution that supports both Clear and Purge methods as mentioned in the NIST 800-88 guidelines. BitRaser also offers two types of verification options namely, total and random. As a NIST Tested & Approved software it ensures compliance with NIST standards and provides verification options, reaffirming that the data is properly sanitized and cannot be retrieved. This gives you mental peace and provides a shield from data security-related lawsuits.