NPI commonly includes the following details of a customer:
- Social Security number
- Personal income
- Marital status
- Details regarding investments and savings
- Loan details
- Deposit balance
- Biometric data
- Asset Information
- Credit Card History
- Bank account details
GLBA ensures the protection of the above information & safeguarding the same, providing consumers with the right to 'opt-out' of specific data-sharing practices. The act regulates any institution significantly engaged in financial activities and lays guidelines on how to handle their customers’ NPI. The Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act is implemented by FTC, which defines NPI as any “personally identifiable financial information” that a financial institution collects about an individual with regard to providing a financial product or service unless that information is otherwise “publicly available.” NPI includes any information that a customer shares with a financial institution to get a product or service. It also includes data generated through transactions between the customer and the financial institution or arising from services the institution provides to the customer. Additionally, NPI covers any information acquired by the financial institution in the course of its operations.
Applicability of GLBA – Professions & Businesses
The Act covers all companies or professions designated as "financial institutions" and may include:
- Insurance services
- Investment guidance
- Financial advisors
- Check-cashing business
- Credit card facilities
- Payday lenders
- Loans like student, personal, or business loans
- Mortgage brokers
- Nonbank lenders
- Debt collection
- Personal property or real estate appraisers
- Online money transfer
- Professional tax preparers
- Courier services, etc.
Key Sections & Provisions of the GLB Act
The key objective of this act is to ensure the confidentiality of customers' financial information by implementing proper privacy and security standards as defined in Title V- Privacy of the GLB Act. The Act has 3 major Rules – Safeguard Rule, Privacy Rule, and Pretexting Rule.
- Section 501 – Financial Safeguard Rule – Protection of NPI
As per Sec 501 (a), all businesses covered under the Act must respect the privacy of their customers & define a policy for safeguarding the same. Section 501(b) requires financial institutions to implement appropriate safeguards to protect consumer data. Agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and OCC (Office of the Comptroller of the Currency) must establish these safeguards for the financial institutions under their jurisdiction. These should cover the physical, technical, and administrative safeguards to:
- Ensure confidentiality and security of customer information and records.
- Protect against any anticipated threats or hazards to records' security or integrity.
- Protect against unauthorized use or access to records or information that could cause significant inconvenience or harm to a customer.
Note: The Safeguards Rule was amended by the FTC on May 13, 2024, as the 'Final Rule'. The amendment requires financial institutions to report to the Commission if any unencrypted customer information of 500 or more people is accessed without permission.
FTC, under Code of Federal Regulations - Title 16, Commercial Practices, Chapter 1- Subchapter C, Part 314, lays procedures to implement the Financial Safeguard rule. This rule establishes clear standards for protecting customer information, requiring financial institutions to develop, implement, and maintain a detailed information security program to ensure the security and confidentiality of NPI.
- Section 502: Privacy Rule provides details about the obligations a financial institution has w.r.t. disclosure of NPI. It states that the NPI must not be disclosed to a non-affiliated third party unless:
- The same has been conveyed to the consumer by the financial institution in a clear manner, in written or electronic form or any other form permitted by the regulation.
- The customer is given the opportunity to refuse disclosure of their information to the third party before it is disclosed.
- The consumer has been informed how to opt out of sharing their information.
- Section 503 requires financial institutions to disclose their privacy policy and practices clearly and conspicuously to their customers. This disclosure must happen when the customer relationship is established or at least once a year during the relationship. This policy disclosure must contain information related to the following:
- Institutional policies regarding disclosure of NPI to non-affiliated third parties, along with the category of people to whom the NPI will be disclosed.
- Policy regarding disclosure of NPI of persons who are no longer customers of the financial institution.
- Categories of NPI collected.
- Financial institution's policies for protection of customers' NPI.
The disclosures must take place according to the Section 504 - Rulemaking.
FTC implements the 'Privacy Rule' through the Code of Federal Regulations - Title 16, Commercial Practices, Chapter 1, Subchapter C - Part 313. FTC governs how financial institutions treat their customers' NPIs. It also provides information on privacy and opt-out notices, limits on the disclosure of information, the relation of this part to other laws, and exceptional cases.
- Section 521- Pretexting Rule: These provisions are covered under Subtitle B - Fraudulent Access to Financial Information, and prohibit obtaining or attempting to access someone else's financial information by lying, using fake, forged documents, or providing false information to financial institutions or their customers. These provisions have certain exemptions and are not applicable to law enforcement agencies, Insurance agencies investigating insurance frauds, or private investigators when it is necessary to collect overdue child support.
- Section 522 (a) covers the Administrative Enforcement of GLBA by various federal bodies. Some of the federal agencies that can enforce provisions of GLBA are:
- FTC
- OCC
- SEC
- Board of FDIC
- Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
- Office of Thrift Supervision
- National Credit Union Administration
- State Insurance Authority
Consequences and Penalties for Non-compliance to GLBA
GLBA non-compliance penalties can be quite serious for financial institutions. They include both monetary fines and imprisonment. Section 523 explores the criminal penalties, which are:
- Intentional or unintentional violation or attempted violation of Section 521 will result in a fine according to Title 18 of the US Code or imprisonment for a maximum of 5 years, or both.
- Suppose breaking Section 521 is combined with breaking other US laws or being involved in illegal activities involving sums of up to $100,000 in a year. In that case, the penalty can include a fine of double the amount specified in Section 3571 of Title 18, up to 10 years in prison, or both.
Non-compliance also means damage to the organization's reputation. In the past, companies such as PayPal and Venmo had also faced GLBA non-compliance issues and had to reach settlements with the FTC.
Recommendations to Meet Compliance with GLBA
Following are some of the key considerations to attain compliance with the act in order to protect customer information:
- Appoint specific people within the organization to implement and maintain the information security program as per GLBA guidelines.
- Determine and evaluate the risks to customer information.
- Design and set up a data safeguard program and routinely monitor and evaluate it.
- Partner only with those affiliates that can maintain the required standard checks.
- Ensure that the contract compels partners to maintain safeguards for protecting NPI.
A significant provision of the act is anchored on safeguarding customers' nonpublic personal information through the implementation of an information security plan. The Safeguards Rule identifies three key areas for ensuring information safety and, thereby, compliance, which include Employee Management and Training, Information Systems, and Detecting and Managing System Failures. In these areas, Information Systems deal with the collection and storage of NPI, i.e., what information is being collected, how it is stored, and whether there is a business need to collect the information.
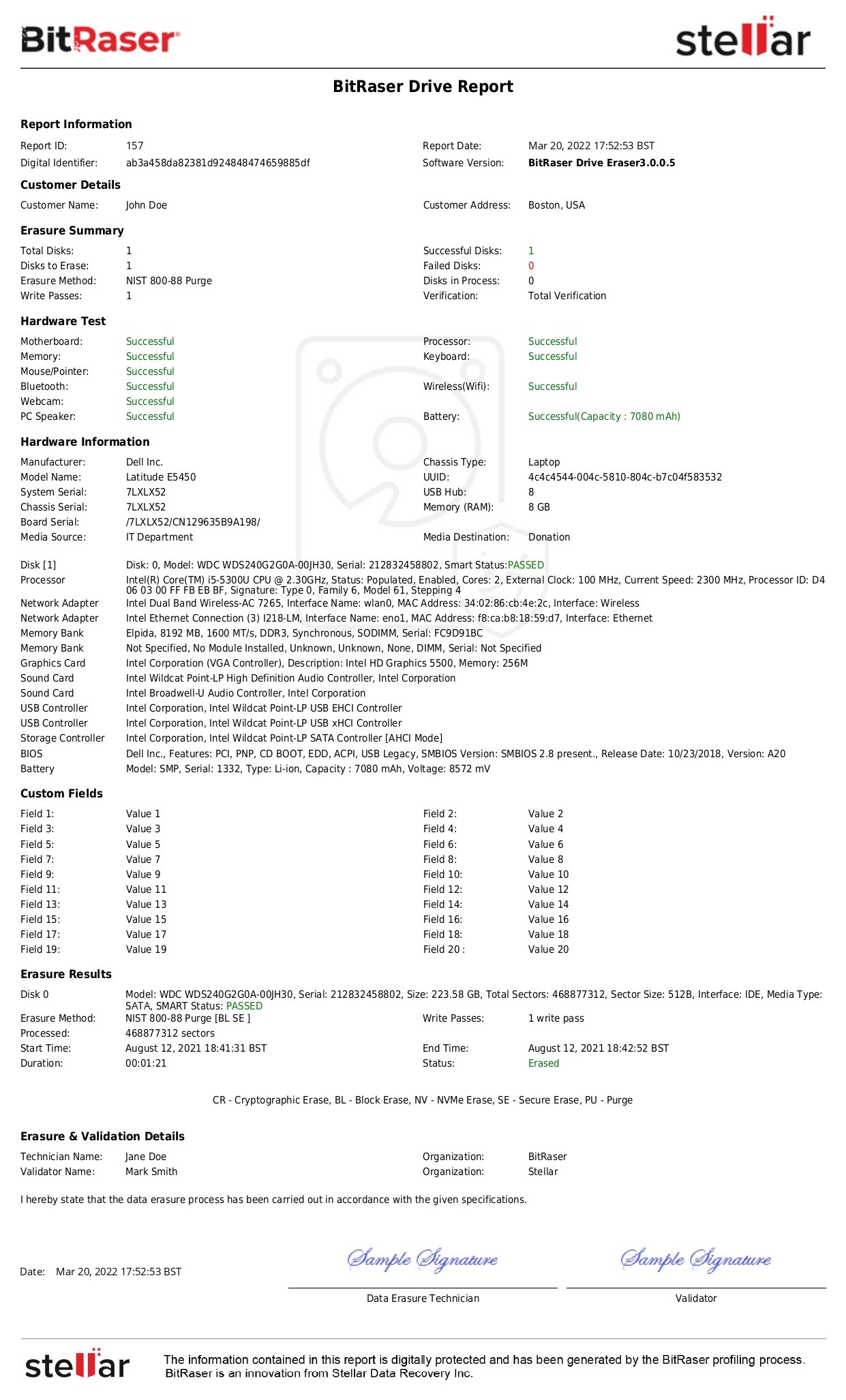
Data erasure technology can help businesses meet compliance needs concerning this Information Systems provision in the Safeguards Rule of GLBA. Software tools such as BitRaser can permanently erase all unwanted or redundant NPI to safeguard the data from breach or unauthorized exposure.