Degaussing is the technique of demagnetizing magnetic storage media devices such as tapes, floppy disks, and hard drives. When the magnetic properties of the storage media are destroyed, no information can be read from it, making it inaccessible. Degaussed media can no longer be used due to destruction in its fundamental property to store data. Due to this, a degaussed hard drive or a magnetic tape cannot be reused, making it pose environmental-sustainability concerns as a method of data destruction.
How Does Degaussing Work?
In the process of degaussing, a strong magnetizing field is generated using a device called a degausser. This magnetic field neutralizes or rearranges the magnetic field orientation of the storage media that is being degaussed. This renders the data on the storage device unreadable and the data irretrievable. Though degaussing hard drives is generally considered extremely effective, its efficacy depends on the magnetic field strength of the degausser. However, if the coercivity of the magnetic media is higher than the magnetic field strength (measured in Gauss) of the degausser, then data on the device won’t get erased in an efficient manner. Coercivity (measured in Oersteds) is the strength of a magnetic storage media to resist the attempt to modify its magnetic properties.
To understand more about degaussing, its pros and cons, read our article: What is Degaussing: Pros, Cons and Alternative.
Is Degaussing SSDs Effective?
As mentioned above, the coercivity of the magnetic storage media decides the efficacy of degaussing. However, SSDs and SEDs are NAND-based flash storage media that use chip-based technology with no moving parts; hence, degaussing does not work on them. In fact, using a degausser on an SSD can damage the device physically without actually erasing the data. A data recovery laboratory can retrieve the sensitive data from the damaged SSD that was degaussed. The success of the data recovery completely depends on the extent of the damage caused by the degausser.
NAND-based flash memory includes Single Level Cell (SLC), Multi-Level Cell (MLC), Triple Level Cell (TLC), Quad Level Cell (QLC), and 3D NAND flash memory cannot be erased using degaussing. 3D NAND is also referred to as Vertical NAND or V-NAND. Degaussing SSDs using any of these NAND-based flash memory arrangements is futile. Before taking a decision to degauss SSDs, IT admins must understand how degaussing works and the fact that chip-based technology is totally different from magnetic media technology that can be degaussed. Further, degaussing is also ineffective on HDDs that have a higher coercivity than the gauss level of the degausser.
Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR) and Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording (MAMR) use heat and microwaves, respectively, to catalyze the magnetic recording process, enabling higher data storage densities. Since they are more stable, demagnetizing them is a tough task raising questions regarding the effectiveness of the degauss method. While several manufacturers and providers of media sanitization equipment inform that HAMRs cannot be degaussed and degaussing MAMRs depends on the gauss level of degaussers, the National Security Agency/Central Security Service (NSA/CSA) requires the use of incineration to destroy HAMR/MAMR drives. According to the NIST SP 800-88 media sanitization guidelines, degaussing no longer applies in the cases of most flash memory-based storage devices.
Alternative Methods to Destroy Data on SSDs
SSDs have gained more prominence in recent years because of their high write and erase speeds along with high endurance. Degaussing SSDs is an ineffective method of data sanitization; in other words, there is no way to degauss SSDs. However, there exist other alternate methods to destroy data sanitization methods that can be useful in removing data from SSDs permanently.
Among physical data sanitization methods such as burning, incinerating, disintegrating, and pulverizing, the most widely applied is –
- Shredding: This process involves shredding the storage media into pieces of the smallest size. If the shredder is unable to shred the SSD into bits of a recommended size, then the possibility of data recovery remains. However, with the rise of miniaturization, shredding an already small-sized storage media into smaller bits can be a challenge. The blades or teeth of the shredder cut the media into strips. Many shredders have a screen attached to provide a crosscut.
IEEE 2883-2022 states that, “It is acceptable to incorporate pulverize and shred methods as an interim destruction step prior to shipping storage media for further processing such as melt, incineration, or disintegration.” The ADISA ICT Asset Recovery Standard recommends checking the screen aperture during audits and the maximum shred particle size for verification of shredding.
However, it is to be noted that shredding is a physical data destruction method that renders the device unusable and is against the principle of a circular economy. Even if the device is to be shredded, the recycling of the material extracted post-shredding must be done in the right manner preferably using a certified ITAD like CompuCycle dealing with SSD or hard drive shredding.
Logical data sanitization is compatible with most types of storage media including SSDs and flash-memory-based media, and hence, is an effective way to sanitize data. The various types of logical data sanitization are explained below:
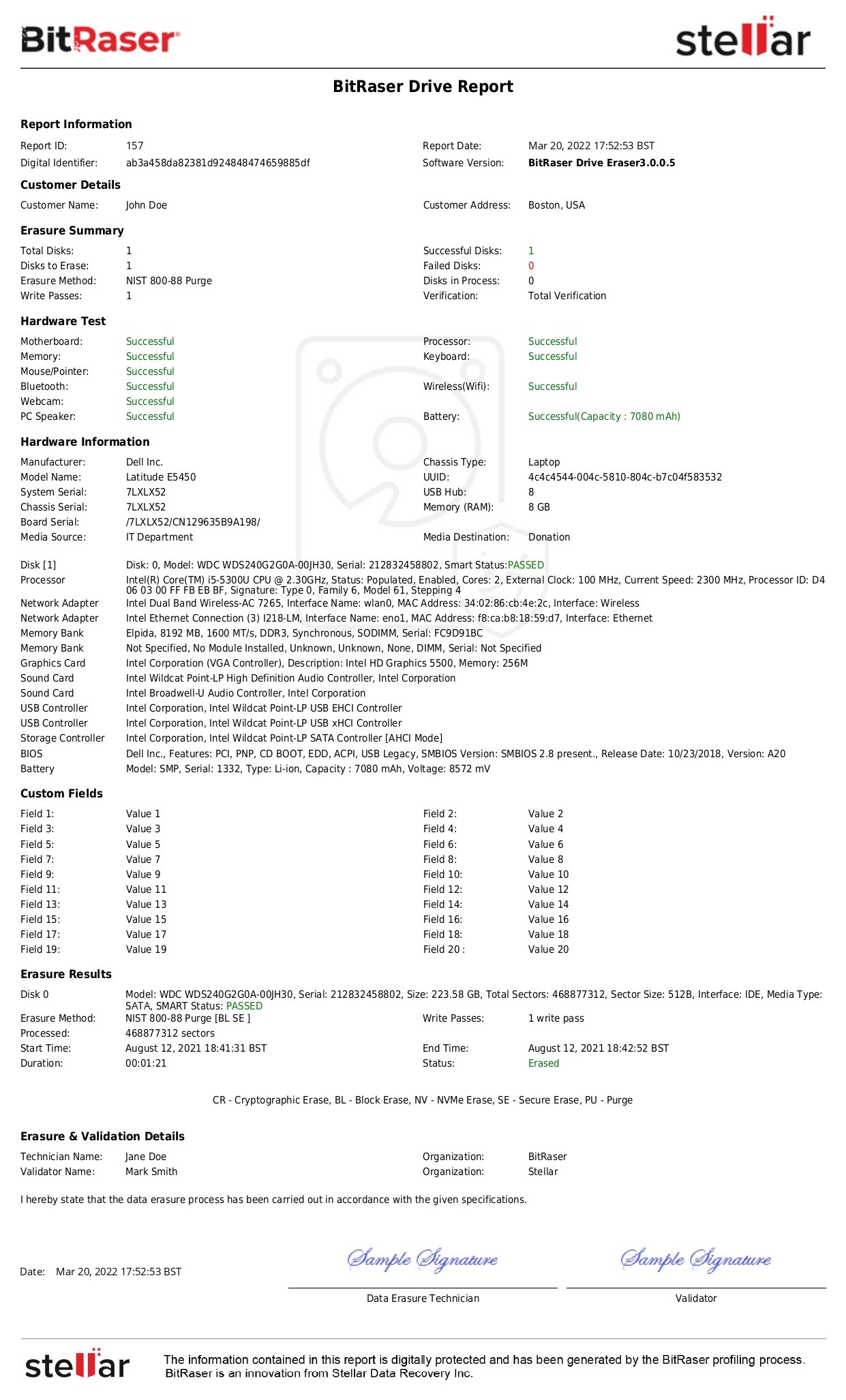
- Data Erasure: This process involves overwriting existing data with 0s, 1s, or pseudo-random digits. This permanently removes the sensitive information by making it unintelligible. A software-based data erasure program like BitRaser applies approved algorithms like NIST Clear, DoD (1 pass), NIST Purge, etc., to ensure data is irrecoverable. Use of approved algorithms enables achieving compliance with data protection laws and regulations. Unlike most physical destruction methods whose efficacy cannot be verified, verification of data erasure can be done by software like BitRaser Drive Verifier. It ensures no trace of data remains on the media after it has been wiped.
- Block Erase: This procedure erases data in blocks and replaces the block with the values set by the vendor. It is faster than overwriting and is usually applied to semiconductor storage media such as NAND-based flash storage media.
- Cryptographic Erase: This data sanitization method erases the cryptographic key instead of the location where the data is stored. It is appropriate for devices like SEDs or drives that are encrypted using hardware encryption mechanisms. When the Media Encryption Key (MEK) is erased, there is no way to access the original data, thereby ensuring data is irrecoverable.
In a Nutshell
The most sought-after alternative to degaussing an SSD is to erase them using a software-based data sanitization method that is both environment-friendly and compliant with global data protection laws. To keep up with the data sanitization requirements of the modern storage media, data erasure is the best choice that businesses can make.