According to BBC, "Millions
of storage devices are being shredded each year, even though they could be
reused." Using professional data erasure software for destroying
data boosts a circular economy and promotes sustainability by reusing the
device rather than physically destroying it.
What is Data Destruction Software?
Data Destruction
software is used for permanently destroying data from drives and devices such as a hard drive, SSDs, PCs, laptops, Macs, & Android & iOS-based mobile devices, making it unrecoverable. Data destruction tools use multiple techniques to wipe clean drives and devices. They are sometimes
referred to as data wiping, data sanitization, or data erasure software.
Different methods to destroy data have been defined by international bodies
such as NIST, DoD & IEEE 2883 to ensure proper data destruction methods are used based on the media type.
The top data destruction methods include Logical methods like Overwriting, Cryptographic Erase (CE), Secure Erase (SE), and Block Erase. Physical methods, on the other hand, include degaussing, shredding, and pulverizing. The physical method is detrimental to the environment as it destroys the device and contributes to e-waste. It should only be used as a last resort for inaccessible drives and devices with bad sectors. The preferred method is Overwriting, Block Erase or Crypto Erase. Read our in-depth article on Methods of Data Destruction.
Global data protection laws
like GDPR, CCPA, PDPA (Singapore), PDPA (Philippines), PIPEDA, and POPIA
regulate data collection, processing, storage, handling, disposal, and how it
is shared by data processors & data collectors. Therefore, organizations
must carefully frame their data destruction policy and define
the data destruction software to be used organization-wide while disposing of
end-of-life IT assets or while repurposing or reallocating them. It is
important to carefully assess the software capabilities in terms of
functionality, scalability, erasure standards supported, certificate of destruction produced, and verification methods supported. Let's look at some
of the benefits of data destruction software.
Benefits of Data Destruction Software:
Data destruction
software has numerous benefits that can be leveraged by organizations to
protect their sensitive and confidential information. The major benefits of
using data destruction software are listed below:
- Helps Maintain Compliance: Permanent data destruction helps organizations fulfil the data disposal mandates of global data protection and privacy regulations, laws and standards like EU-GDPR, CCPA, PCI-DSS, FACTA, ISO27001, etc., thereby ensuring compliance.
- Avoiding Data Security Breaches: Eliminating redundant, obsolete, and trivial data minimizes potential attack vectors, reducing the risk of exploitation by cybercriminals and preventing data security breaches.
- Avoiding Penalties: Any unintentional violation by the organization can lead to massive penalties. For Example, GDPR infringement can result in fines of up to Euro 20 million or up to 4% of the global turnover, whichever is higher.
- Build Trust: Having a data destruction policy helps organizations showcase their commitment to responsible data management practices, which helps them gain the trust of their employees, customers, investors, and other stakeholders.
- Preventing Reputational Damage: The data destruction tool securely eliminates sensitive data, ensuring zero risk of leakage and safeguarding against reputational damage caused by data breaches or leaks.
- Helps Save Cost: Data erasure promotes the recycling and reuse of devices and helps reduce operational costs and resource conservation.
- Helps Meet ESG Goals: Physically destroyed devices end up in landfills and contribute to land, air, and water pollution. Data erasure software, on the other hand, is a proponent of the 'Zero Landfill' movement because the wiped device is recyclable and reusable, thus helping organizations meet ESG goals.
Features of a Professional Data Destruction Software:
The
following are some of the key features of an effective data erasure software
for securely wiping data
- Secure & Complete Data Removal: A data destruction tool must securely and completely erase data from storage media, making it impossible to recover even in a data recovery laboratory setting.
- Support for Multiple Drive & Device Types: Organizations store data on a multitude of storage media like HDDs, SSDs, USBs, PC, Laptops, Macs, Chromebooks, MS Surface, Servers, etc. A robust data wiping software must support erasure from a wide range of devices.
- Support for Erasing Devices Remotely: The software must be able to remotely wipe data from devices at physically spread-out locations, especially in work-from-home cases.
- Performs Erasure Verification: The professional data wiping tool must be able to verify the success of the data erasure process as per NIST 800-88 guidelines by using Random or Total verification methods.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: The tool should be able to support multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
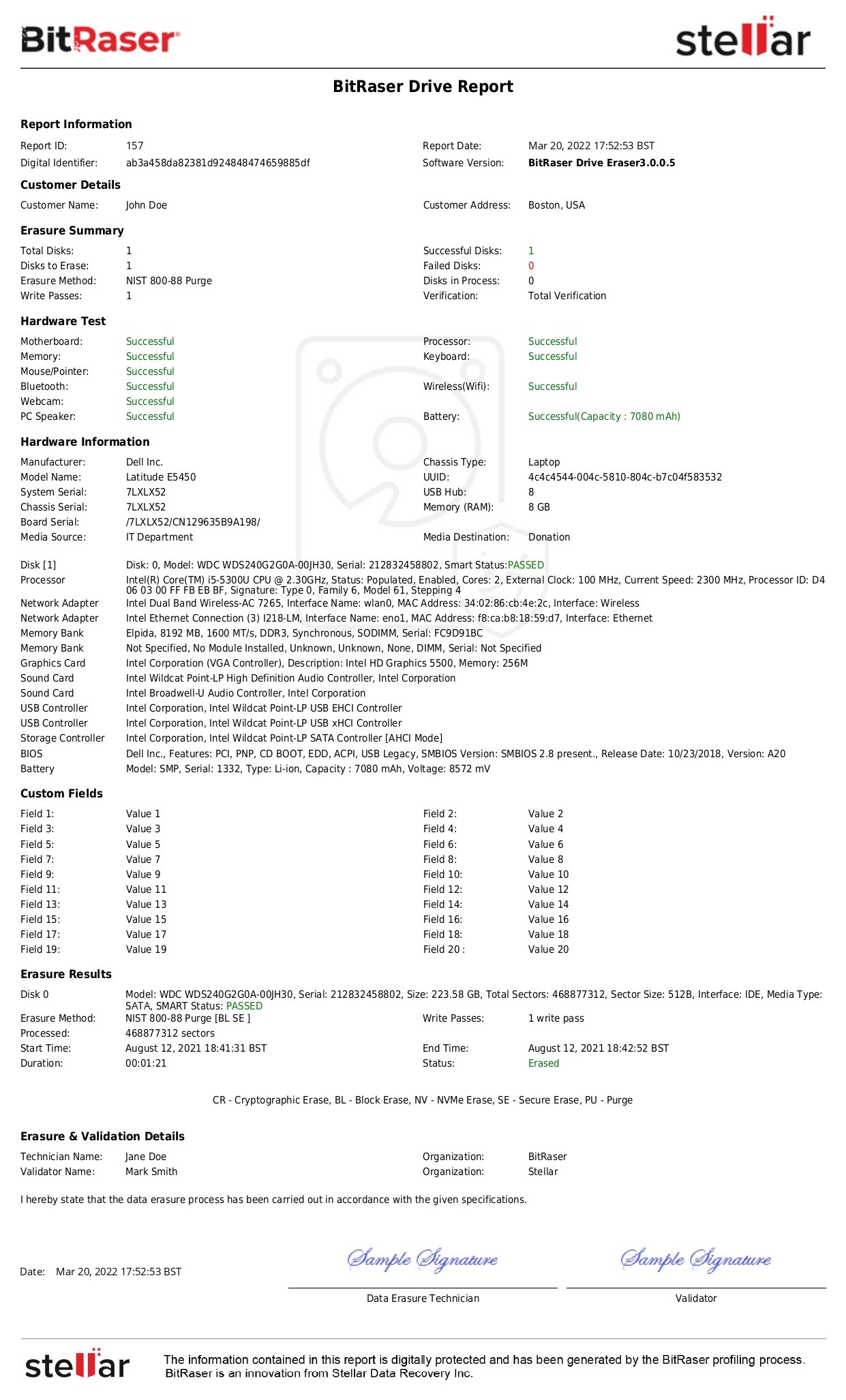
- Generates Certificate of Destruction (COD): A professional data wiping software must generate data destruction certificates and erasure reports containing details of the erased device, the erasure method used, the verification technique applied, and information about the data wiping technician. These certificates must be available electronically for any time, anywhere access. These are vital for meeting the compliance requirements of regulations like SOX, GLBA, HIPAA, FACTA, etc.
- Provides Scalability & Automation: A data erasure software must offer flexibility to technicians to automate and deploy it over a network or use it on a standalone device. BitRaser is one such solution from Stellar that allows erasing 65,000 drives over a network via PXE boot using the Network Cloud variant. To know more about the BitRaser Drive Eraser variants, you can read our article.
- Integration with Asset Management Applications: Organizations use asset management tools to track their IT inventory. A seamless integration of data destruction software with asset management tools ensures that data-wiping records are stored at the same location.
- Support and Updates: Last but not least, the software must be regularly updated to align with the latest technological advancements and changes in OS versions.
Recommended Data Erasure Tool:
BitRaser data erasure software helps erase data securely from all drives and devices and is a highly recommended data destruction tool for enterprises, governments, ITADs, and service providers. It has all the features of professional data destruction software and helps in meeting compliance with data protection laws & regulations.