Responsible Use and Recycling or R2 Standard focuses on regulating the impact of electronics refurbishing and recycling on the environment and workers associated with the e-recycling industry. Originated in North America in 2008— the Standard is widely adopted by electronic recyclers, including IT Asset Disposition companies (ITADs), refurbished, and resellers for sustainable electronics recycling in an eco-friendly way through the Test, Repair, Reuse, and Recycling stages.
R2v3, released in July 2020 by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International (SERI), is the second major revision or upgrade of the R2 Practices since 2013, when the first revision was released. According to the R2 version 3.0 documentation (© SERI, 2020: The R2 Standard by SERI Version 3 (R2v3)), R2 certification can help IT Asset Managers, buyers of IT asset destruction, refurbishing and remarketing services, and recyclers to reinforce confidence on sustainable & safe management of used electronics equipment. Further, ITAD companies having R2v3 certification are in a stronger position to assure customers of the efficacy of their data destruction practices.
This article outlines the R2v3 core requirements, focusing on the "Data Security" requirement that chiefly concerns the IT asset destruction industry.
R2v3 Introduction— The Core Requirements
The R2v3 requirements span ten different areas, ranging from scope, responsible e-waste management strategies, and legal requirements to data security, facility requirements, and more. The following is a brief outline of the latest R2v3 requirements:
1. Scope
This requirement mandates an R2 Facility to determine and certify the processes, electronic equipment, component, and material streams managed. It also brings activities like collection, renewal, repair, remarketing, disintegration, asset recovery, brokering, and recycling of used electronic items within the scope of R2v3 certification.
2. Hierarchy of Responsible Management Strategies
This requirement area specifies the need for developing and adhering to a policy for managing used and end-of-life electronic equipment, components, and materials. It mandates the policy to include hierarchical & responsible management strategies that prioritize reuse, followed by recovery and recycling.
3. EH&S Management System
This requirement area in R2v3 directs the R2 Facility to maintain a certified Environmental, Health, and Safety Management System (EHSMS) that allows planning, implementing, and monitoring the environmental, health, and safety practices w.r.t the safety of workers, the public, and the environment under both normal and exceptional circumstances. It requires an R2 facility to periodically review and evaluate associated risks of exposure to hazardous substances like mercury, lead, beryllium, cadmium, etc.
4. Legal & Other Requirements
This requirement in the R2v3 Standard focuses on meeting compliance with the prevailing laws for environmental safety, health, and data security concerning the processing, transit, and import or export of electronic equipment, components, and materials.
5. Tracking Throughput
As per this requirement area, an R2 Facility shall record and manage the throughput of all electronic equipment, components, and materials and keep adequate documentation mentioning the details of the movement of all the electronic items.
6. Sorting, Categorization, and Processing
This area defines the requirement for assessing, organizing, and categorizing the electronic equipment as per the R2 Equipment Categorization reference. An R2 Facility is required to develop and maintain a process document in order to conduct the sorting and categorization of electronic equipment before it gets processed. It also requires defining of instructions and criteria considering if the components can be reused basis their physical conditions and functionality.
7. Data Security
This R2 Facility is required to maintain high standards of data security by ensuring high levels of security and sanitization of all data storage devices based on the device type and data sensitivity. Meeting the R2v3 "Data Security" requirement is crucial for attaining safe and compliant data destruction outcomes. And therefore, the requirement is a critical consideration area for ITAD companies wanting to scale up their practices and attain compliance in line with R2 version 3. In a later section, we cover the R2v3 Data Security requirement, including critical updates that impact ITAD operations.
8. Focus Materials
This requirement is concerned with the management of on-site processes and the hiring of e-recycling vendors to ensure that the focus material passing through the facility does not affect the health and safety of workers, the public, and the environment.
9. Facility Requirements
As per this requirement, the R2 Facility should process and store electronic equipment, components, and materials in a legally compliant manner. Also, the processing and storage of electronic equipment should not affect the health and safety of workers, the public, and the environment.
10. Transport
This area specifies the standards for safe and legally compliant transportation of electronic equipment, components, and materials considering physical media and data security, workers' health and safety, and environmental impact.
Demystifying the R2v3 Data Security Requirement for ITAD Companies
The Data Security requirement (Core 7) identifies four areas for meeting R2 compliance, namely:
1) Documentation
This aspect emphasizes the need for detailed documentation on the data sanitization plan and procedures. The documentation should comprise the following details:
- Security mechanism to protect data in the R2 Facility's control, including the declaration of the secure & access-restricted areas dedicated to data sanitization.
- Types of data storage devices and data the R2 Facility is going to sanitize.
- Presence of network services that could automatically restore the data on the devices
- Methods used for sanitizing the data based on the device type
- Planned duration to destroy the data after receiving it
- Third-party vendors hired to perform data sanitization, including those providing services in another country
- Documented records that demonstrate the efficacy of data sanitization and verification methods Process for approving and monitoring workers, visitors, etc., who are allowed access to data-bearing devices.
The Requirement also mandates a written and maintained data security policy to govern the following actions:
- Prohibit unauthorized access to data storage devices
- Appoint a competent Data Protection Representative with the overall responsibility and authority for the R2 Facility's data security and legal compliance
- Report known and alleged data and security breaches to the Data Protection Representative
- Training and authorization of personnel before they handle data storage devices
- Determine the penalty for non-compliance with the data security policy
2) Security
The Security aspect of R2v3 deals with controlling physical access to the data storage devices in an R2 Facility as per the following guidelines:
- An R2 Facility should implement a security program to regulate access to data storage devices based on the electronic equipment, data sensitivity, and needs of the suppliers.
- The R2 Facility should implement security authorization levels to control access for workers, visitors, etc., based on the data storage device type and data sensitivity.
- The R2 Facility should maintain a written acknowledgment of responsibility from individuals who are granted access to restricted areas.
- Implement an incident response procedure to investigate & report data breach incidents to the suppliers, legal authorities, and other parties concerned as per the law.
3) Process
This aspect focuses on defining the processes followed for receiving and sanitizing data storage devices, including process audit, as follows:
- The R2 Facility receiving any data-bearing equipment or component should provide the supplier with a receipt for those devices.
- The R2 Facility should also provide details of the data sanitization method to be used for the equipment, and whether data sanitization will be done internally or by a vendor.
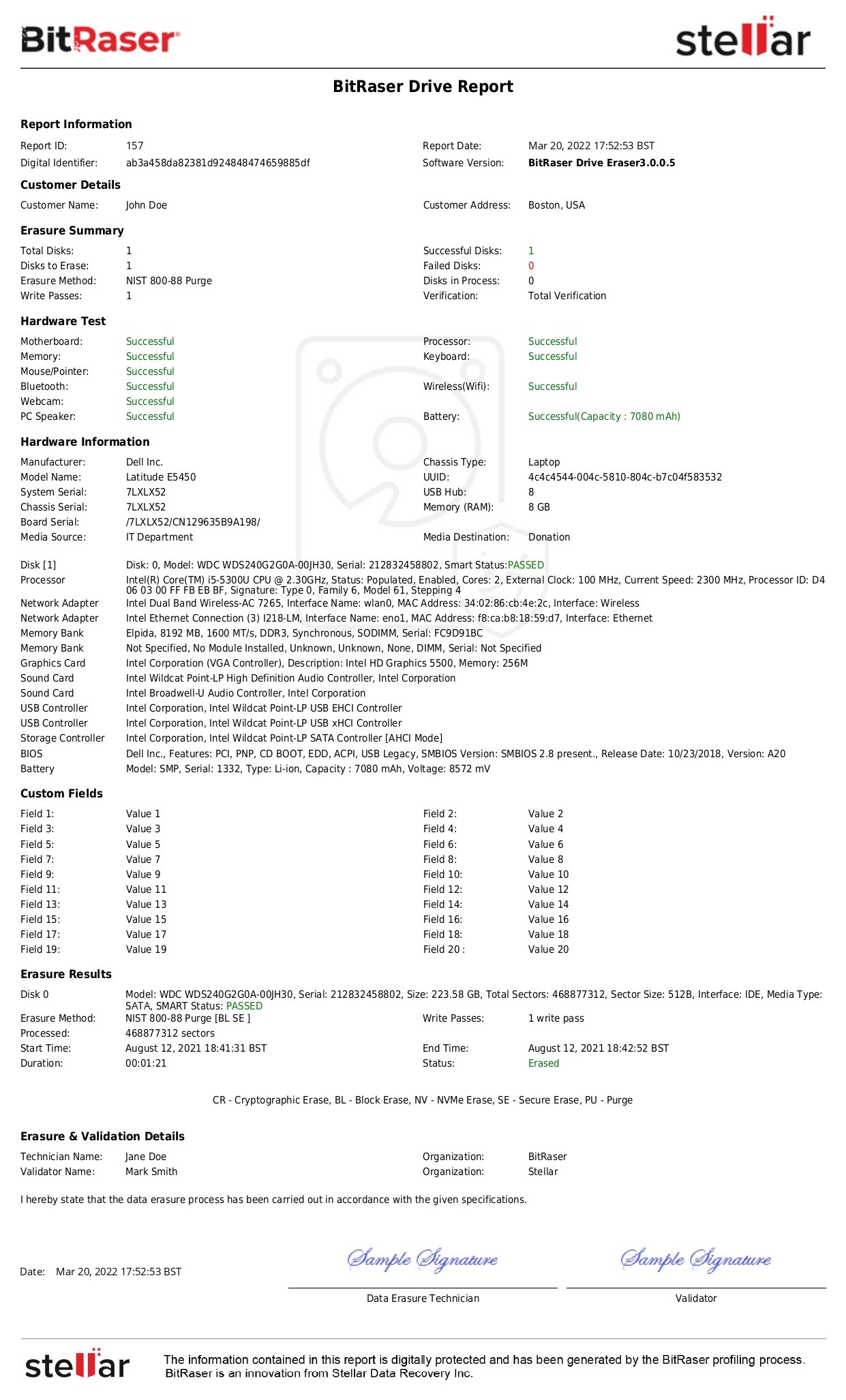
- All data must be sanitized unless the supplier requests otherwise in accordance with R2 Standard. All data storage devices should be sanitized timely and effectively based on the methods disclosed to the supplier while receiving the equipment. R2v3 documentation prescribes data sanitization in accordance with Appendix B – Data Sanitization.
- For physical destruction methods, the R2 Facility should follow the NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines and verify the results to ensure 100% effectiveness of the data destruction method.
- For data storage devices shipped to a vendor, the R2 Facility should verify the vendor for media sanitization capabilities in accordance with the planned method.
- Conduct a data security and sanitization audit at least once every year by a competent auditor to validate process effectiveness and compliance with R2 Standard, legal norms, and the data sanitization plan.
4) Notifications
This aspect of the R2v3 Data Security requirement mandates the R2 Facility to have a process for notifying the suppliers, legal authorities, and other third parties in the event of —
- Any changes in downstream vendors responsible for processing data storage devices
- Data breach incidents
R2v3 Appendix B — Data Sanitization Process Requirement
The R2v3 Standard provides specific guidelines for data sanitization using physical destruction and logical sanitization (data erasure) methods. Adhering to these methods is crucial for ITAD companies seeking compliance with the R2v3 Standard.
While the R2 physical destruction requirements are primarily based on NIST SP 800-88 Guidelines, the data erasure guidelines are specific to the R2 Standard and apply to particular areas, as follows:
a) Data Erasure Software:
The data erasure software used should wipe all user-addressable memory locations on the data storage media. Also, the software should be able to fail the media if it cannot erase any user-addressable memory location.
b) Electronic Records of Data Sanitization:
Electronic data erasure records should be maintained for all the storage devices logically sanitized (overwritten) using the data erasure software. The wiping records should map to the unique identifier for the data storage media.
c) Removal of Login & Passwords:
R2 requirements for data erasure mandate the removal of all the logins, passwords, locks, or any other mechanism that could allow access to the storage media.
Data Erasure Software: Leap Forward to R2v3 Compliance for ITADs
The R2 Standard defines sweeping requirements to help IT asset destruction, e-recycling, and refurbishing companies meet the prevailing norms for environmentally safe and sustainable e-recycling practices.
"Data Security" or Core 7 is a critical requirement in R2v3, focusing on maintaining data security by sanitizing the used or end-of-life data storage devices. The requirement specifies physical destruction and data erasure as the two methods for media sanitization. Further, it emphasizes the need for effective sanitization (i.e., erasure of all user addressable memory locations) and electronic data erasure records.
Professional data erasure software can help ITAD companies meet compliance with logical media sanitization standards as per the R2v3 Data Security requirement. By wiping all addressable memory locations, including the hidden areas, and generating tamper-proof digital reports of erasure, the tool can help ITADs meet R2v3¬ data security compliance and data sanitization process requirements. To know more about how software can help you comply with R2v3 standards, you may write to [email protected].