Summary: Cyber attackers use vulnerabilities in networks, systems, and storage media to gain access to and attack businesses. Understanding the stages of an attack and the potential outcome can help organizations prepare for contingencies. Read this article to learn about these vulnerabilities and ways to safeguard against them.
Cyber-attacks have become more frequent in the last few years, and all organizations that store data must have a comprehensive data protection strategy to mitigate the risks arising due to vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability and its manifold triggers have alarmed Network Administrators and System Administrators, alike. And, with digital transformation, vulnerability has also emerged as a serious security concern for Data Administrators. The organizations’ growing focus on digital transformation, in general, has largely pushed the Big Data realm with the massive generation of user data which is difficult to manage and secure. Consequently, this has exposed numerous loopholes for cyber attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information on a network or standalone system.
What is Vulnerability?
The term vulnerability defines an underlying weakness associated with a system, which if not patched in time, exposes the system to a potential threat. For example, failing to patch Windows updates on a Web server is a vulnerability.
Stages of Data Vulnerability
Data is continuously exposed to cybersecurity threats due to several types of vulnerabilities which manifest in the following stages:
- At the Network level: USB Thumb Drives, Laptops and Netbooks (Contain an Ethernet port to tap directly into the network), Wireless Access Points, the unsupervised person in the server room (Trojan humans), digital assets, and more.
- At the System level: Email phishing, a fellow being watching the user during login, Top 3 most exploited programs installed on a system include – Adobe Reader, Oracle Java, and Adobe Flash At the Data level: unsecured mobile devices, unsecured Cloud Storage systems, and more.
- At the Data level: unsatisfied employees, unsecured mobile devices, storage applications including cloud, unsecured systems at third-party service providers, hackers, and more.
Most businesses have heterogeneous systems with multiplatform automated patching to guard the networks and systems closely. But, sometimes, the administrators are unable to assess the type of vulnerability, which initiates a vast majority of threats due to unpatched networks and systems. A small vulnerability at an entry-level network, when left unattended, may thus turn out to be the most feasible loophole for malicious attacks on an organization.
Therefore, plugging these vulnerabilities -before they get traced by a malicious entity -is one of the best preventive measures to protect data and stop such entry-level network threats from branching out to multiple risks.
Impact of Data Vulnerability
1. Business Downtime: The downtime or outage happens when a system becomes unavailable for a certain duration and fails to perform its primary function. To restore a compromised system from scratch, the business has to invest resources, which causes upfront loss.
Downtime also leads to business disruption when critical IT systems are involved, especially the database where there are higher chances of organizational data being compromised. According to Ponemon's cost of data breach study, organizations based in the US can recover some of the highest post-breach response costs.
2. Data loss: Data encryption by ransomware might cause permanent loss of data, thus, compromising strategic advantage and affecting brand reputation and overall business health. In cases of encryption, you need data recovery software like Stellar Data Recovery. Data loss prevention could have been possible if the organizations had applied timely patches.
3. Data privacy and legal implications: Unauthorized 3rd party data access affects the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of organizational data, thereby compromising data privacy. In today’s context, non-compliance with data privacy regulations such as the GDPR might lead to legal complications.
How to Safeguard Against Data Vulnerabilities?
This is possible! By taking adequate preemptive measures at -
- Network-level
- System-level
- Data level
1. Network Level Security:
- Implement Unified Threat Management (UTM) to ensure perimeter security around Firewalls and Routers, and apply for phishing protection, etc.
- Patch updates that are suggested during vulnerability tests, and address the vulnerabilities based on the order of priorities– critical, high, medium, and low –to prevent malicious attacks.
- Stateful packet inspection to clearly distinguish legitimate network communication from malicious communication. Apply real-time packet decryption software for regular packet checks.
- Establish Virtual Private Network (VPN) for secure private connection over public network links.
2. System Level Security:
- Monitor hardware assets —Network Switches, Routers, Servers— and software performance by using online monitoring tools such as Opsview, Nagios, etc. to keep the risks arising out of system discrepancies at bay.
- Perform regular maintenance to improve the availability, scalability, safety, and reliability of physical assets, and ensure better protection.
- Maintain data backup at different physical locations to retrieve the data affected due to an unexpected malicious attack. Since the backup is not on the same network, there are almost nil chances of the data getting affected.
3. Data Security:
- Advanced-Data encryption: Encryption is not a new thing, but today’s encryption must be implemented in a more strategic & systematic way to protect data from cybercriminals and insider threats. You want to rely on an encryption system that not only prohibits outsiders from coming in but also ensures that a system administrator or other inside source can’t be at a low level in the operational system.
- Implement role-based access control for individual documents: Organizations have to enable data sharing for employees, partners, third-party vendors, consultants and auditors, and other professionals associated with their business. To have proper security controls, it is a must to implement role-based access control down to the individual level documents.
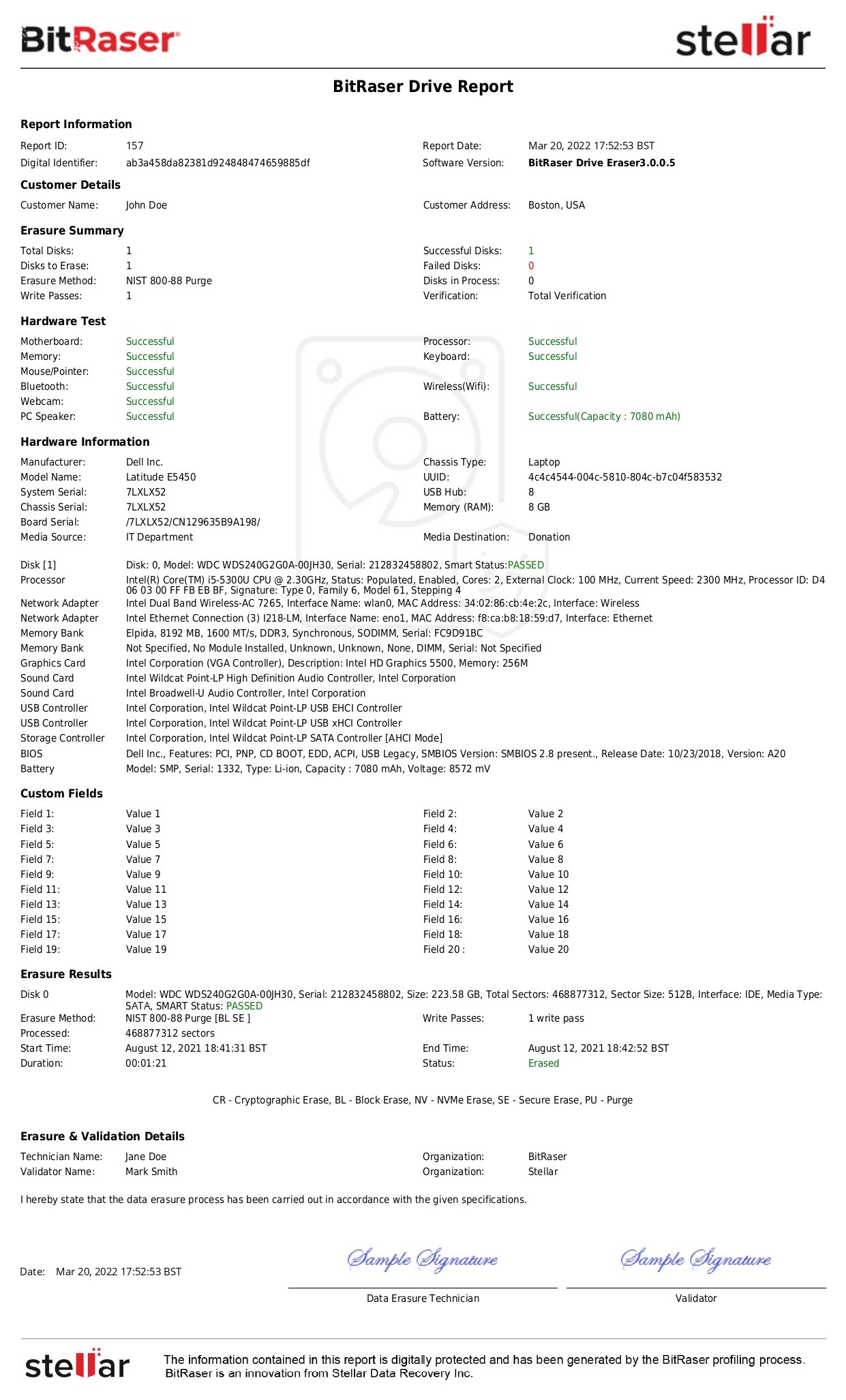
- Data Erasure: Sensitive information when not in use must be erased from the systems to free up space and (more importantly) avoid exploitation by hackers. Data erasure software such as BitRaser helps erase redundant and non-useful data from multiple IT assets in one go.
A data erasure software like BitRaser can help organizations and individuals safeguard sensitive data in the following ways:
- Erase confidential information when not in use
- Erase browsing history, cookies, system and application traces
- Erase email client data on Windows and any other system in use when IT Asset changes hands
- Erase files-shortcuts from USBs and other storage media
While Data Protection is largely based on implementing preventive measures and practices, Data Disposition is concerned with the safe disposal of redundant or undesired data. And there are regulatory policies to govern safe data disposition, which mandate organizations to comply with privacy and security standards. In this regard, data erasure software such as BitRaser is used by Enterprises to perform secure data erasure in line with international standards. BitRaser erases sensitive data in an efficient, cost-effective, secure, and socially responsible manner during the recycling or relocation of data assets.
Don’t be the victim! Use secure data erasure software today
Not just for erasure, certified data erasure software like BitRaser helps organizations plug vulnerabilities and protect their network and systems from many threats arising out of data exposure.