The term ‘degaussing’ is derived from the unit of magnetism, Gauss, which is named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, the German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to the field of magnetism. Degaussing is a traditional data destruction technique applicable to only magnetic storage media such as hard disk drives (2.5 and 3.5 inches), floppies, tape drives (LTO, DLT, AIT, QIC), etc. This technique demagnetizes or neutralizes the magnetic properties present on the surface of the storage media.
Visualize the magnetic storage media as a large "magnetized surface" split into several tiny sub-micron magnetic regions using a strong local magnetic field generated using a media writing head. These magnetized domains have their own local and uniform field orientations used for storing the data. This process eliminates these local magnetic domains by neutralizing their field orientations, thereby rendering the data unreadable.
How is Degaussing Performed?
Degaussing requires a specialized device that applies a strong magnetic field to rearrange or randomize the existing polarity of the storage media. As a result, the data recorded on the magnetized domains of the storage media is corrupted or destroyed. Its efficacy depends upon its magnetic field strength vis-à-vis the media it is degaussing. Its magnetic field strength is measured in Gauss. Typically, the degausser must have higher coercivity than the magnetic media to degauss it effectively. Coercivity is the magnetic media's (here, Hard Disk Drives: HDDs) resistance to alterations in its magnetic field orientation. It is measured in a unit called Oersteds (Oe).
Degaussers can have varying magnetic field strengths: 10,000 Gauss, 50,000 Gauss, etc. Modern storage media have a coercivity of around 5000 Oe. For example, a degausser of 1.1 Gauss can sanitize a magnetic media of 1 Oe.
Note: If the magnetic field strength and magnetic orientation of the degausser are insufficient, then media sanitization would be unsuccessful. Hence, storage media with high coercivity is tougher to degauss.
There are essentially three types of degaussers based on the mechanism they use to generate the magnetic field which are as follow.
- Coil Degausser: This comprises a copper wire wound on a steel core. The setup produces a strong electromagnetic field when it is connected to electricity. This electromagnetic field demagnetizes the magnetic storage media completely and hence, destroys data.

Image 1: Coil Degausser
- Pulse Degausser/Capacitive Discharge Degausser: This device stores electrical charge in a capacitor, discharging the energy as a strong high-frequency electromagnetic pulse to demagnetize the storage media. This process degausses the magnetic storage media, thereby destroying the data.

Image 2: Capacitive Discharge Degausser
- Permanent Magnet Degausser: The permanent magnet degausser requires one or more natural rare-earth elements with magnetic properties like neodymium and works without electricity. When magnetic media designated to be sanitized is placed in a special arrangement with these metals having extremely high field strengths, the media is degaussed.
Pros of Degaussing
- It is an effective physical media sanitization method for magnetic storage media like HDDs only. It permanently destroys data and the degaussed device. Generally, it is recommended by government authorities where data security is crucial. Degaussing is approved by NSA and DoD as a classified data destruction method.
- It is a fast process with many degaussers offering a degauss cycle of less than 60 seconds per drive.
Limitations of Degaussing
There are specific shortcomings of degaussing, crucial for consideration while defining an organization's data destruction strategy, as follows:
- Limited to Magnetic Media: Degaussers cannot sanitize IT assets with embedded drives, flash memory-based storage media such as Solid-State Drives (SSDs) or other non-magnetic storage media. Does Degaussing work on SSDs? elaborates more on the subject.
- Low Efficacy of Data Destruction: Degaussers need to have sufficient magnetic force, carefully matched with the media coercivity, to perform degaussing successfully. Their efficacy is also based on the equipment type and their appropriate usage, electromagnetic or permanent magnet degaussers. The NIST SP 800-88 guidelines clearly state that “assurance provided by degaussing depends on selecting an effective degausser, applying it appropriately, and periodically spot-checking the results to ensure it is working as expected.” If the degausser lacks higher coercivity, then it does not work efficiently even on modern HDDs.
- Renders Device Unusable & Creates E-Waste: Degaussing turns magnetic storage media like HDDs including IDE, EIDE, ATA, and SCSI drives useless. These unusable devices conflict with the goals of a circular economy. It also creates e-waste violating the requirements of the environmental protection laws and regulations. This affects the organization’s efforts in reducing their impact on the environment, ranking poorly on their sustainability reports.
- Requires Specialized Equipment: Degaussers can be expensive and require skilled professionals to operate them. This increases the Total Cost of Operations (TCO) even if only a minimal number of drives need to be degaussed. For example, the cost of NSA-evaluated degaussers with high oersted values can range between US $5000 and $40000, incurring a significant operational expense. This cost can further add up for organizations with media sanitization needs spread across multiple facilities or branches.
- Less Scalable: Degaussers are designed to sanitize a low number of storage media at a time, allowing less scalability. For organizations requiring hundreds of drives to be sanitized at once, degaussing is an inefficient technique with a slow turnaround and considerable manual effort and time consumption.
Degaussing Alternative: Secure Data Erasure
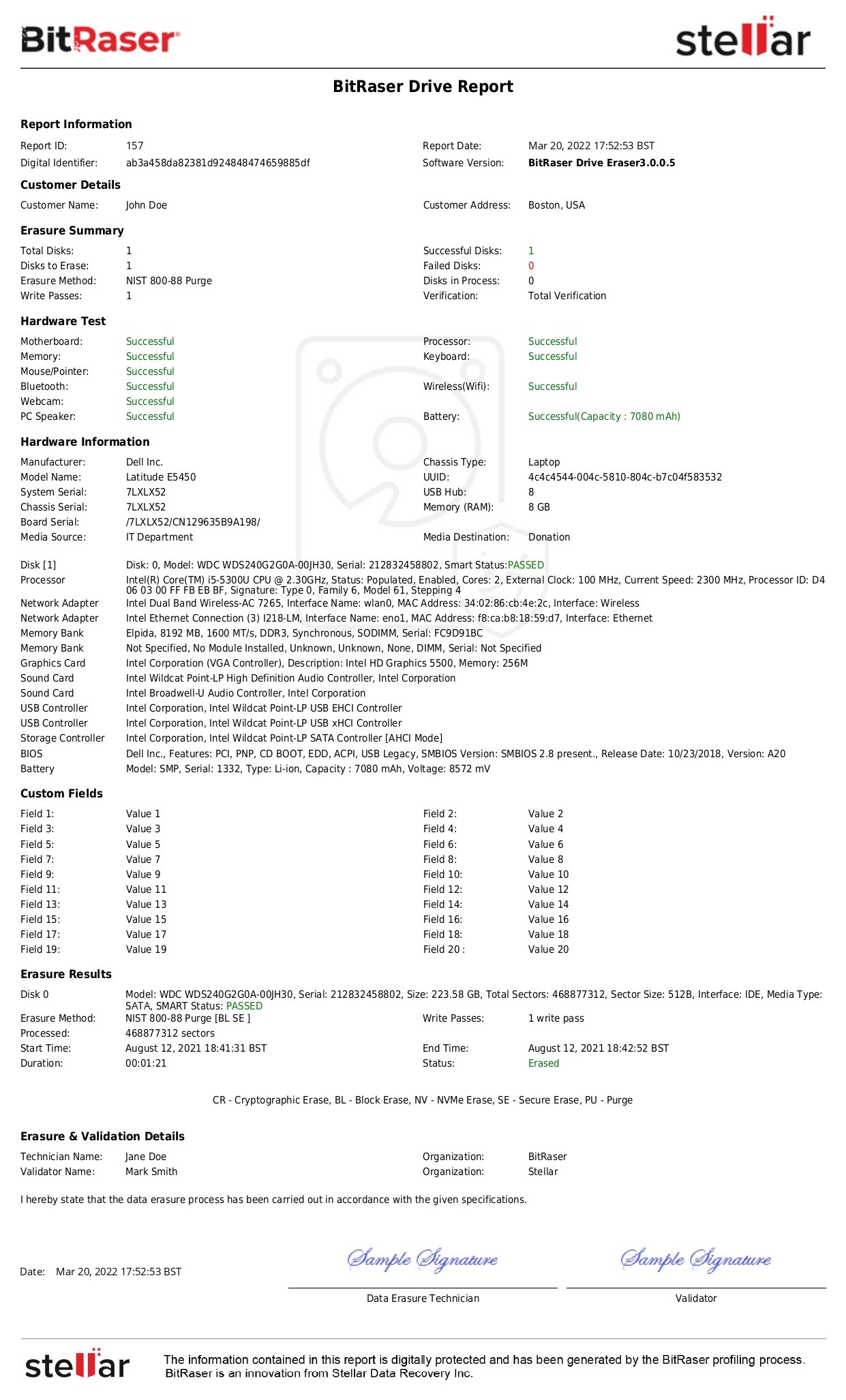
Data erasure or data wiping is a media sanitization technique based on overwriting the user-addressable and hidden memory locations on a storage drive with binary patterns like 0s and 1s. Data wiping also includes techniques like Cryptographic Erase, Secure Erase, and Block Erase that fall under the NIST Purge data sanitization method. The erasure technique destroys the data and renders it irrecoverable using single or multiple overwriting passes following specialized data-wiping algorithms. Further, it verifies the data sanitization to confirm the wiping efficacy against the desired outcomes.
Some of the inherent benefits of secure data erasure as an alternative to degaussing are listed below:
- Wider Media Supported: The software-based data erasure technique can sanitize a wider variety of storage media, including magnetic storage like Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and flash storage media: drives like SSD, NVMe, etc., and embedded devices like MacBooks, tablets, mobile devices, etc. Organizations can wipe data from laptops, PCs, servers, and Chromebooks using a robust and scalable data erasure tool like BitRaser that generates a proof of data destruction and also verifies data sanitization.
- Effective Irrespective of Coercivity: The magnetic field or incompatible coercivity value of a storage media does not impact the efficacy of a data erasure solution. Data erasure software works independently of the OS and the device’s properties. It performs erasure by following data-wiping standards such as NIST 800-88 Clear, NIST Purge, and US-DoD 5220.22-M that define how the data is to be overwritten to make it irrecoverable.
- High Scalability and Manageability: Professional data erasure software can erase thousands of storage drives simultaneously. In contrast with degaussing, which allows limited parallel media sanitization capacity, data erasure software allows extensive scalability to meet the needs across the usage spectrum. BitRaser Drive Eraser (Network Cloud Variant) can erase up to 65000 drives and devices together in a single workflow. Further, with add-ons like a centralized cloud console, the tool provides manageability of systematic wiping across locations by customizing the erasure application.
- Generates Zero E-waste and Allows Media Reuse: There is no e-waste generation as the erased media is re-assimilated for active usage unless it is an end-of-life or legacy asset that needs recycling. Data erasure is environmentally sustainable, unlike degaussing, and plays a crucial role in promoting a circular economy. The erased storage drive can be reused immediately with no impact on its residual value. Data erasure prepares a thoroughly sanitized storage hardware asset, ready for reallocation, exchange, return, donation, refurbishment, resale, etc.
- Ease of Deployment: Data Erasure can be pre-customized and applied seamlessly across boundaries; it can be downloaded from any location, whereas a degausser has to be physically present to perform degaussing. What's more, with the prevalence of remote work environments post-COVID-19, degaussers cannot be sent to remote employee locations to destroy data in case of mass layoffs or contract termination. Remote Data Wiping Software is the wise solution in the case of remote work environments and comes as a cost-effective solution.
- Economical: Data erasure is a cost-effective solution making it more affordable for businesses. The total cost of operation is very low in the case of data erasure compared to degaussing.
Takeaway
Although an established media sanitization technique, degaussing has become an outdated technique for sanitizing flash-memory-based media. It is also completely ineffective for evolving storage media with higher coercivity, including modern-day HDDs. Software-based techniques like data erasure that follow the overwriting technique provide a more effective, expansive, and scalable alternative. It equips organizations with a broader capability to wipe storage media with assurance.